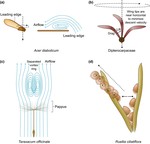
Dandelion pappus morphing is actuated by radially patterned material swelling
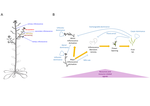
The dandelion pappus changes shape when it is wet. This is due to a unique ring of tissue in the centre of the structure that swells in …
Shoot dominance relationships lead to robust reproductive outputs
The number of reproductive structures produced by Arabidopsis and Brassica is consistent regardless of branching patterns. …
The fat of the land: cuticle formation in terrestrial plants
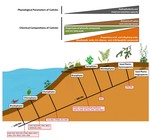
Cuticle composition changes during land plant evolution from largely phenolic-based in bryophytes to dicarboxylic acid-based …
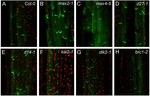
Callose deposition during pollen development
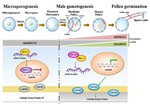
A SKU5-SIMILAR family protein in cotton regulates callose deposition during pollen formation.
Informed dispersal of the dandelion
Why do the parachutes (pappi) of dandelion fruits close when wet? Fluid flow and drag forces are significantly altered when this …
The conserved plant PM19 protein functions as an osmosensor and regulator of germination
PM19-like proteins are present across land plants. The Arabidopsis PM19L1 can complement the osmosensitivity of the yeast Sho1 mutant …
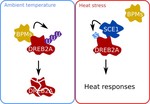
Hot on the trail of DREB2A protein stability
Posttranslational modification of DREB2A stabilises it to modify heat stress responses.
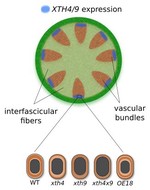
Cell wall remodeling during wood development
Xyloglucan endotransglycosylases impact on cell wall remodeling of secondary cell walls.
From passive to informed: mechanical mechanisms of seed dispersal
Plants use a variety of physical mechanisms to disperse their fruits and seeds. Some of these mechanisms can respond to environmental …
Design principles of hair-like structures as biological machines
Plants use a variety of physical mechanisms to disperse their fruits and seeds. Some of these mechanisms can respond to environmental …
BRC1 expression regulates bud activation potential but is not necessary or sufficient for bud growth inhibition in Arabidopsis
We analyse the role of a transcription factor in shoot branching and investigate how its expression relates to plant hormones and …
Strigolactone regulates shoot development through a core signalling pathway
The plant hormone, strigolactone, regulates shoot branching. We investigate the roles of several potential strigolactone targets in …